1. Introduction:
This text primarily introduces the sensible software of LIMO Cobot by Elephant Robotics in a simulated state of affairs. You could have seen earlier posts about LIMO Cobot’s technical instances, A[LINK], B[LINK]. The explanation for writing one other associated article is that the unique testing setting, whereas demonstrating primary performance, usually seems overly idealized and simplified when simulating real-world functions. Due to this fact, we intention to make use of it in a extra operationally constant setting and share among the points that arose at the moment.
2. Evaluating the Outdated and New Eventualities:
First, let’s take a look at what the previous and new eventualities are like.
Outdated State of affairs: A easy setup with a number of obstacles, comparatively common objects, and a subject enclosed by limitations, roughly 1.5m*2m in dimension.
New State of affairs: The brand new state of affairs accommodates a greater diversity of obstacles of various shapes, together with a hollowed-out object within the center, simulating an actual setting with highway steering markers, parking areas, and extra. The scale of the sphere is 3m*3m.
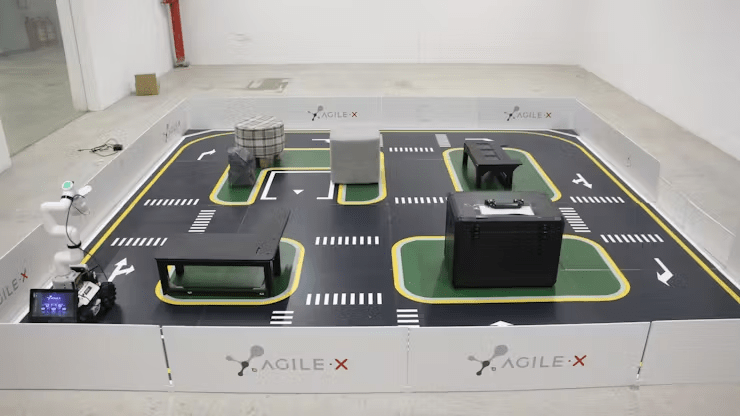
The change in setting is important for testing and demonstrating the comprehensiveness and applicability of our product.
3. Evaluation of Sensible Circumstances:
Subsequent, let’s briefly introduce the general course of.
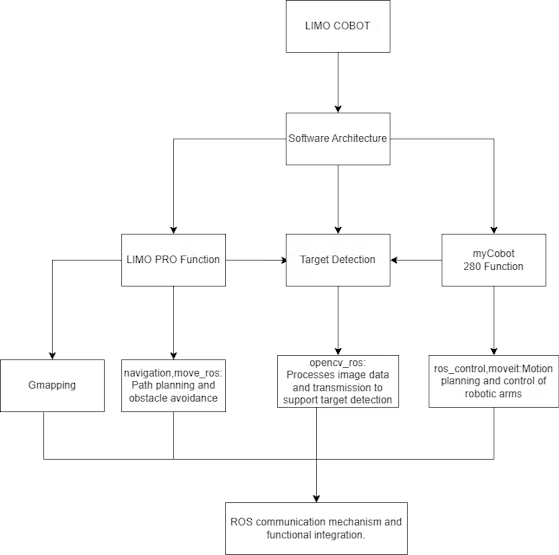
The method is especially divided into three modules: one is the performance of LIMO PRO, the second is machine imaginative and prescient processing, and the third is the performance of the robotic arm. (For a extra detailed introduction, please see the earlier article https://robots-blog.com/2024/05/16/exploring-elephant-robotics-limo-cobot/.)
LIMO PRO is especially answerable for SLAM mapping, utilizing the gmapping algorithm to map the terrain, navigate, and in the end obtain the operate of fixed-point patrol.
myCobot 280 M5 is primarily answerable for the duty of greedy objects. A digicam and a suction pump actuator are put in on the finish of the robotic arm. The digicam captures the true scene, and the picture is processed by the OpenCV algorithm to seek out the coordinates of the goal object and carry out the greedy operation.
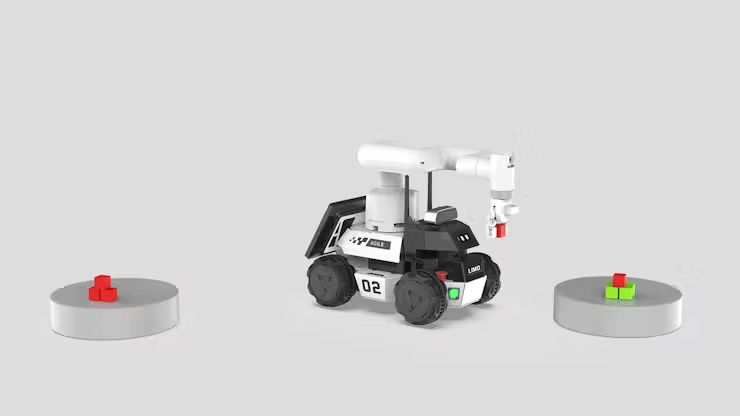
Total course of:
1. LIMO performs mapping.⇛
2. Run the fixed-point cruising program.⇛
3. LIMO goes to level A ⇛ myCobot 280 performs the greedy operation ⇒ goes to level B ⇛ myCobot 280 performs the inserting operation.
4. ↺ Repeat step 3 till there are not any goal objects, then terminate this system.
Subsequent, let’s comply with the sensible execution course of.
Mapping:
First, you have to begin the radar by opening a brand new terminal and getting into the next command:
roslaunch limo_bringup limo_start.launch pub_odom_tf:=falseThen, begin the gmapping mapping algorithm by opening one other new terminal and getting into the command:
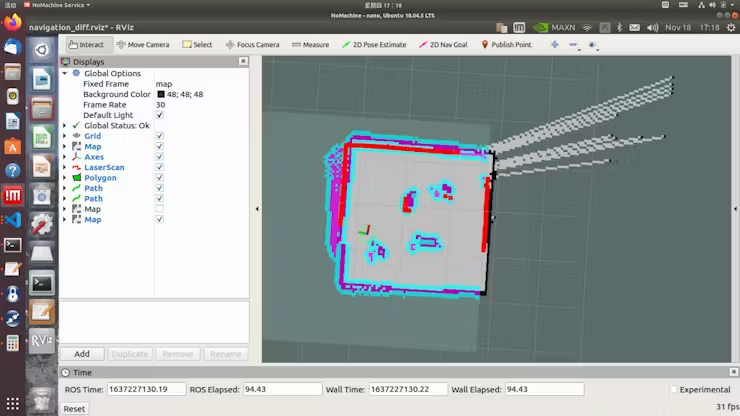
roslaunch limo_bringup limo_gmapping.launchAfter profitable startup, the rviz visualization instrument will open, and you will note the interface as proven within the determine.
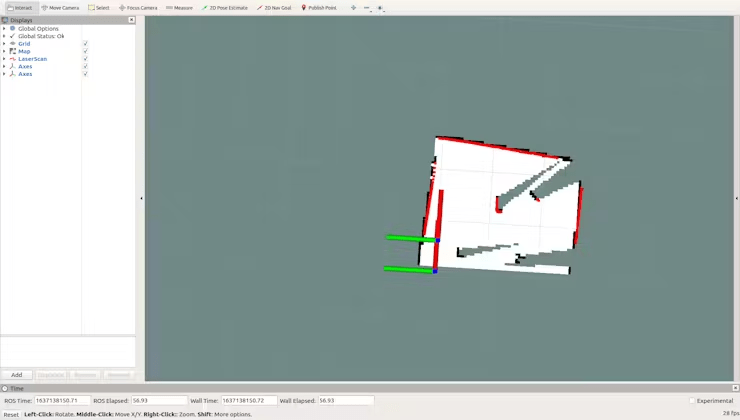
At this level, you possibly can swap the controller to distant management mode to regulate the LIMO for mapping.
After setting up the map, you have to run the next instructions to avoid wasting the map to a specified listing:
1. Change to the listing the place you need to save the map. Right here, save the map to `~/agilex_ws/src/limo_ros/limo_bringup/maps/`. Enter the command within the terminal:
cd ~/agilex_ws/src/limo_ros/limo_bringup/maps/2. After switching to `/agilex_ws/limo_bringup/maps`, proceed to enter the command within the terminal:
rosrun map_server map_saver -f map1
This course of went very easily. Let’s proceed by testing the navigation operate from level A to level B.
Navigation:
1. First, begin the radar by getting into the next command within the terminal:
roslaunch limo_bringup limo_start.launch pub_odom_tf:=false2. Begin the navigation operate by getting into the next command within the terminal:
roslaunch limo_bringup limo_navigation_diff.launchUpon success, this interface will open, displaying the map we simply created.
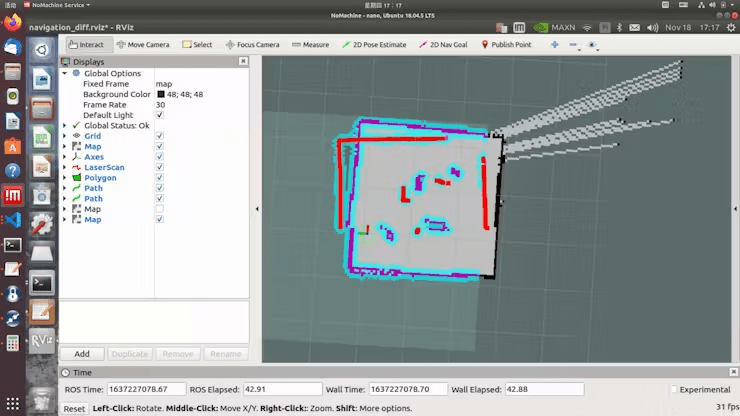
Click on on „2D Pose Estimate, “ then click on on the situation the place LIMO is on the map. After beginning navigation, one can find that the form scanned by the laser doesn’t overlap with the map. That you must manually right this by adjusting the precise place of the chassis within the scene on the map displayed in rviz. Use the instruments in rviz to publish an approximate place for LIMO. Then, use the controller to rotate LIMO, permitting it to auto-correct. When the form of the laser scan overlaps with the shapes within the map’s scene, the correction is full, as proven within the determine the place the scanned form and the map overlap.
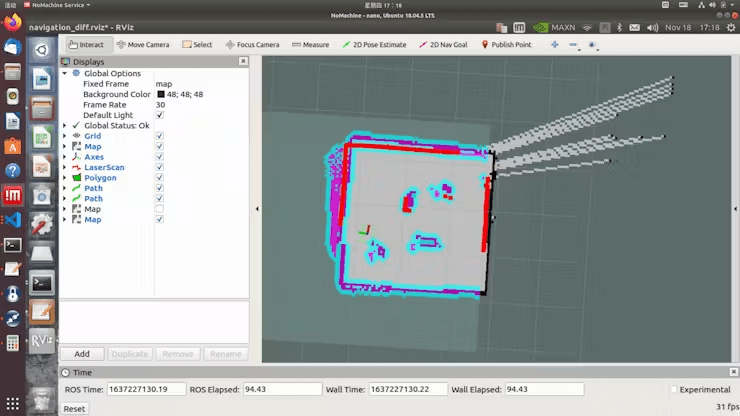
Click on on „2D Nav Purpose“ and choose the vacation spot on the map for navigation.
The navigation check additionally proceeds easily.
Subsequent, we’ll transfer on to the half in regards to the static robotic arm’s greedy operate.
Figuring out and Buying the Pose of Aruco Codes
To exactly establish objects and acquire the place of the goal object, we processed Aruco codes. Earlier than beginning, guarantee the precise parameters of the digicam are set.
Initialize the digicam parameters based mostly on the digicam getting used.
def __init__(self, mtx: np.ndarray, dist: np.ndarray, marker_size: int):
self.mtx = mtx
self.dist = dist
self.marker_size = marker_size
self.aruco_dict = cv2.aruco.Dictionary_get(cv2.aruco.DICT_6X6_250)
self.parameters = cv2.aruco.DetectorParameters_create()Then, establish the item and estimate its pose to acquire the 3D place of the item and output the place data.
def estimatePoseSingleMarkers(self, corners):
"""
This can estimate the rvec and tvec for every of the marker corners detected by:
corners, ids, rejectedImgPoints = detector.detectMarkers(picture)
corners - is an array of detected corners for every detected marker within the picture
marker_size - is the scale of the detected markers
mtx - is the digicam matrix
distortion - is the digicam distortion matrix
RETURN record of rvecs, tvecs, and trash (in order that it corresponds to the previous estimatePoseSingleMarkers())
"""
marker_points = np.array([[-self.marker_size / 2, self.marker_size / 2, 0],
[self.marker_size / 2, self.marker_size / 2, 0],
[self.marker_size / 2, -self.marker_size / 2, 0],
[-self.marker_size / 2, -self.marker_size / 2, 0]], dtype=np.float32)
rvecs = []
tvecs = []
for nook in corners:
retval, rvec, tvec = cv2.solvePnP(marker_points, nook, self.mtx, self.dist, False,
cv2.SOLVEPNP_IPPE_SQUARE)
if retval:
rvecs.append(rvec)
tvecs.append(tvec)rvecs = np.array(rvecs)
tvecs = np.array(tvecs)
(rvecs - tvecs).any()
return rvecs, tvecs
The steps above full the identification and acquisition of the item’s data, and eventually, the item’s coordinates are returned to the robotic arm to execute the greedy.
Robotic Arm Motion and Greedy Operation
Based mostly on the place of the Aruco marker, calculate the goal coordinates the robotic arm wants to maneuver to and convert the place right into a coordinate system appropriate for the robotic arm.
def homo_transform_matrix(x, y, z, rx, ry, rz, order="ZYX"):
rot_mat = rotation_matrix(rx, ry, rz, order=order)
trans_vec = np.array([[x, y, z, 1]]).T
mat = np.vstack([rot_mat, np.zeros((1, 3))])
mat = np.hstack([mat, trans_vec])
return matIf the Z-axis place is detected as too excessive, it is going to be corrected:
if end_effector_z_height just isn't None:
p_base[2] = end_effector_z_heightAfter the coordinate correction is accomplished, the robotic arm will transfer to the goal place.
# Concatenate x, y, z, and the present posture into a brand new array
new_coords = np.concatenate([p_base, curr_rotation[3:]])
xy_coords = new_coords.copy()Then, management the top effector’s API to suction the item.
The above completes the respective capabilities of the 2 robots. Subsequent, they are going to be built-in into the ROS setting.
#Initialize the coordinates of level A and B
goal_1 = [(2.060220241546631,-2.2297520637512207,0.009794792000444471,0.9999520298742676)] #B
goal_2 = [(1.1215190887451172,-0.002757132053375244,-0.7129997613218174,0.7011642748707548)] #A
#Begin navigation and hyperlink the robotic arm
map_navigation = MapNavigation()
arm = VisualGrasping("10.42.0.203",9000)
print("join profitable")
arm.perform_visual_grasp(1,-89)
# Navigate to location A and carry out the duty
for aim in goal_1:
x_goal, y_goal, orientation_z, orientation_w = aim
flag_feed_goalReached = map_navigation.moveToGoal(x_goal, y_goal, orientation_z, orientation_w)
if flag_feed_goalReached:
time.sleep(1)
# executing 1 seize and setting the top effector's Z-axis top to -93.
arm.unload()
print("command accomplished")
else:
print("failed")
4. Issues Encountered
Mapping State of affairs:
After we initially tried mapping with out enclosing the sphere, frequent errors occurred throughout navigation and localization, and it failed to satisfy our necessities for a simulated state of affairs.
Navigation State of affairs:
Within the new state of affairs, one of many obstacles has a hole construction.

Throughout navigation from level A to level B, LIMO could fail to detect this impediment and assume it could possibly go via, damaging the unique impediment. This problem arises as a result of LIMO’s radar is positioned low, scanning solely the empty area. Potential options embody adjusting the radar’s scanning vary, which requires in depth testing for fine-tuning, or adjusting the radar’s top to make sure the impediment is acknowledged as impassable.
Robotic Arm Greedy State of affairs:
Within the video, it’s evident that our goal object is positioned on a flat floor. The greedy didn’t think about impediment avoidance for the item. Sooner or later, when setting particular positions for greedy, this example must be thought-about.
5. Conclusion
Total, LIMO Cobot carried out excellently on this state of affairs, efficiently assembly the necessities. Your entire simulated state of affairs coated a number of core areas of robotics, together with movement management of the robotic arm, path planning, machine imaginative and prescient recognition and greedy, and radar mapping navigation and fixed-point cruising capabilities of the cell chassis. By integrating these practical modules in ROS, we constructed an environment friendly automated course of, showcasing LIMO Cobot’s broad adaptability and advanced capabilities in complicated environments.
Credit